ByWang Zheng, Ni Tao from People’s Daily
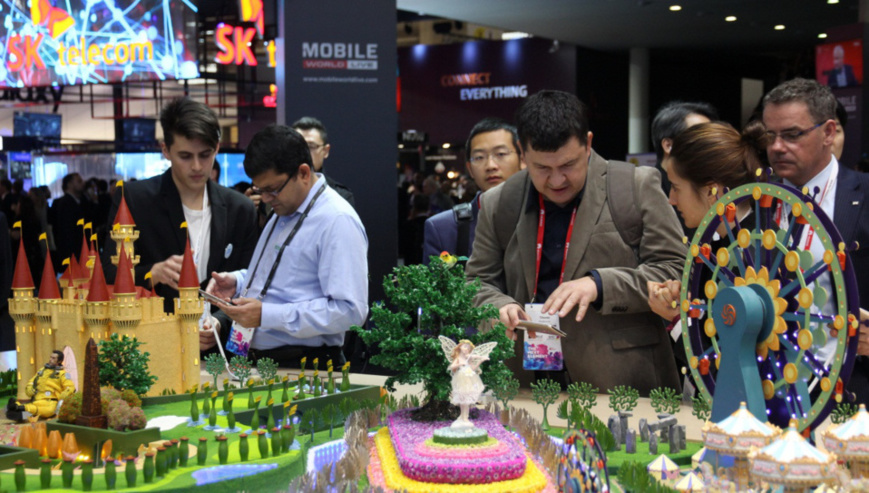

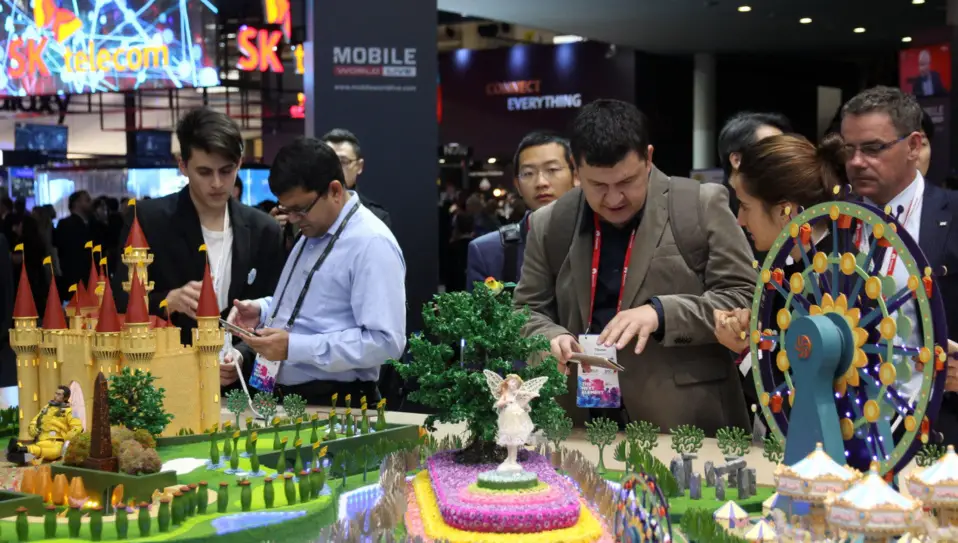
Visitors try newly-released smart phones made by Chinese manufacturer ZTE at the Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona, Spain in February, 2017. (Photo by Wang Di from People’s Daily)
Chinese smart phone brands captured 48 % of global market share in the second quarter of 2017, said a recent report issued by market research firm Counterpoint Research.
According to the report, China’s Huawei has become the world’s third largest mobile phone vendor after Samsung and Apple. In addition, 7 out of the top 10 brands come from China.
Statistics from market intelligence firm International Data Corporation said that Huawei, together with other two Chinese brands Oppo and Vivo,ranked the top three in the domestic market, with a market share of 20.0 %, 18.2 %, and 14.1 %, respectively, in the first quarter of 2017. Apple, which ranked the fourth on the list, held 9.2 % of the market share.
In recent years, Chinese smart phone manufacturers also stepped up their exploration of overseas market based on a good domestic market response.
In addition to the rising share at home, India, the Middle East, Africa, Asia and Europe contributed to therapid growth in the firstthree months of 2017, said Lu Yue, an expert from China Academy of Telecommunication Research.
Lu added that cost-effective performance and reliability are what helped Chinese brands win recognition of young customers in these high-growth markets.
The domain of Samsung and Apple as high-end providers is now challenged by Huawei, whichmanaged to hold a 6% share of the global high-end smart phone market by the end of March. In addition, Oppo and Vivo have improved their share in middle- and high-end markets with advantages in quick-charge, camera, and entertainment.
An increasingly rising investment in research is the major driver of the rapid growth of Chinese phone makers. Data showed that Huawei’s investment in research and development (R&D) grew 37.88 % year on year in 2015. The R&D investment of the company added up to $49 billion in last decade.
In the last five years, the tech giant spent more than 12% of its sales revenue on R&Deach year.
Chinese phone makers also expanded their territory by leveraging both online and offline resources. The rising share of Oppo and Vivo, for instance, can be attributed to their efforts to meet the demands of younger generations in third- and fourth-tier cities.
According to the report, China’s Huawei has become the world’s third largest mobile phone vendor after Samsung and Apple. In addition, 7 out of the top 10 brands come from China.
Statistics from market intelligence firm International Data Corporation said that Huawei, together with other two Chinese brands Oppo and Vivo,ranked the top three in the domestic market, with a market share of 20.0 %, 18.2 %, and 14.1 %, respectively, in the first quarter of 2017. Apple, which ranked the fourth on the list, held 9.2 % of the market share.
In recent years, Chinese smart phone manufacturers also stepped up their exploration of overseas market based on a good domestic market response.
In addition to the rising share at home, India, the Middle East, Africa, Asia and Europe contributed to therapid growth in the firstthree months of 2017, said Lu Yue, an expert from China Academy of Telecommunication Research.
Lu added that cost-effective performance and reliability are what helped Chinese brands win recognition of young customers in these high-growth markets.
The domain of Samsung and Apple as high-end providers is now challenged by Huawei, whichmanaged to hold a 6% share of the global high-end smart phone market by the end of March. In addition, Oppo and Vivo have improved their share in middle- and high-end markets with advantages in quick-charge, camera, and entertainment.
An increasingly rising investment in research is the major driver of the rapid growth of Chinese phone makers. Data showed that Huawei’s investment in research and development (R&D) grew 37.88 % year on year in 2015. The R&D investment of the company added up to $49 billion in last decade.
In the last five years, the tech giant spent more than 12% of its sales revenue on R&Deach year.
Chinese phone makers also expanded their territory by leveraging both online and offline resources. The rising share of Oppo and Vivo, for instance, can be attributed to their efforts to meet the demands of younger generations in third- and fourth-tier cities.
 Menu
Menu
 Chinese smartphone brands capture 48 %%of global market share
Chinese smartphone brands capture 48 %%of global market share