By Gu Zhongyang, Chang Qin, People's Daily
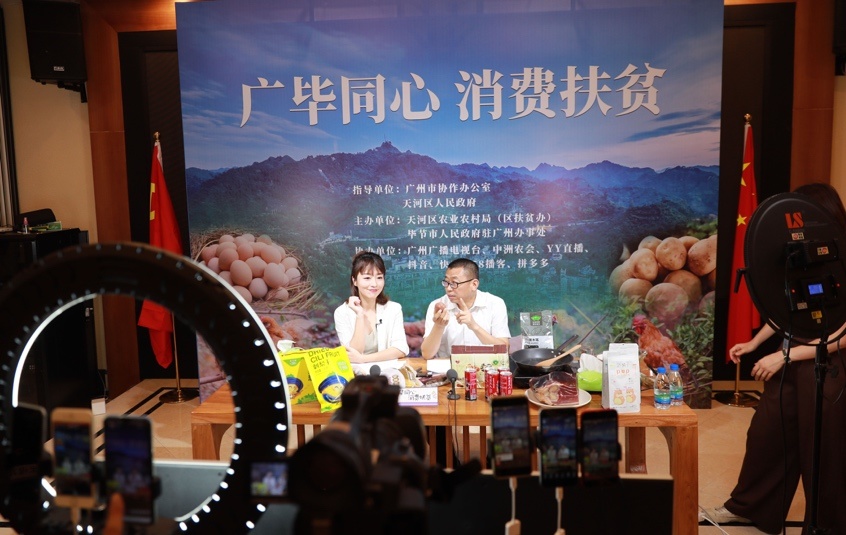

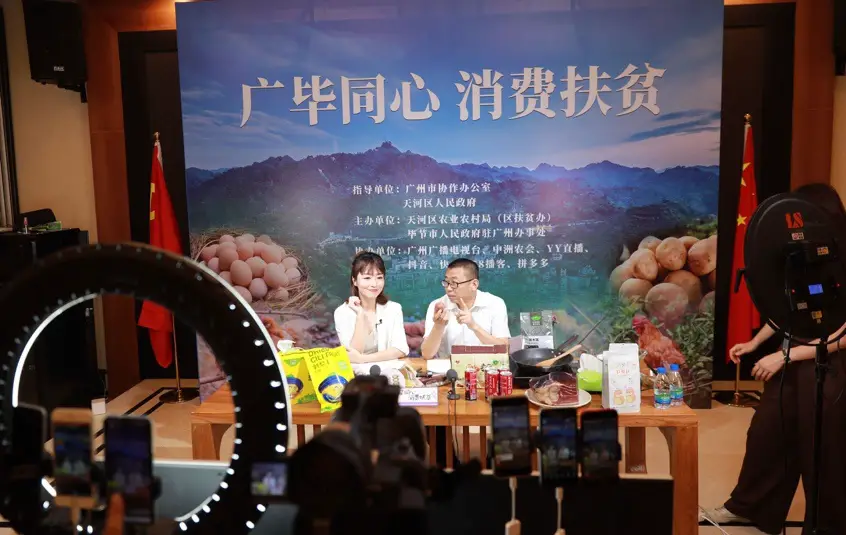
Hosts introduce local agricultural products of Bijie, southwest China's Guizhou province on a livestream show held at a trade center for poverty relief products in Guangzhou, south China's Guangdong province, June 15. (Photo by Han Xianpu/People's Daily Online)
Thanks to Chinese local governments' enhanced efforts to promote pro-consumption campaigns to aid poverty alleviation, more and more farm produces from impoverished regions are getting on the dining tables of the Chinese, paving a road for many households to leave poverty.
These pro-consumption campaigns have effectively opened up the market of agricultural products, offsetting the negative impacts from COVID-19.
A trade fair was recently held in Bozhou, east China's Anhui province to facilitate the sales of local products for poverty alleviation. Nearly 100 kinds of agricultural products from impoverished regions were exhibited at the fair, generating revenue of over 13.5 million yuan ($2.07 million).
Qi Yi, vice general manager of a farm produce company in Anhui, told People's Daily that the company now has employees from more than 100 impoverished households, and the good sale further enhanced its resolution to contribute to poverty alleviation efforts.
In Qixian county, central China's Henan province, impoverished resident Shan Hailong's peanuts and sweet potatoes, which weighed over 5,000 tonnes in total, were hardly sold. To solve his problem, cadres from his village and township immediately introduced him to several local supermarkets, who helped him transport and market his products.
In Nanbu county, southwest China's Sichuan province, a vast orange orchard is cultivated by a local cooperative. According to Luo Qiang, an executive of the cooperative, the orchard is a poverty alleviation program under the coordination between Nanbu county and Dongtou village, Wenzhou, east China's Zhejiang province. The trees are "adopted" by consumers online, and entrusted to the cooperative for management, and the fruits in the orchard all have a QR code that tells their growth and sales.
"Thanks to pro-consumption campaigns to aid poverty alleviation, these fruits are all sold at a pretty good price," Luo said.
The orchard is only one of the many examples of poverty reduction cooperation. A supermarket in Xiamen, southeast China's Fujian province, now runs a special section that sells farm produce from Linxia prefecture, northwest China's Gansu province. "The vegetables from the plateau area enjoy great sunshine and are free from pollution. They taste great," said citizen Zhang Juan, adding that it's also a contribution to poverty alleviation to buy these vegetables.
The pro-consumption campaigns to aid poverty alleviation are never once-for-all deals, and they are gaining more and more returned customers. Luo Zhiyuan from Ji'an, east China's Jiangxi province, is a frequent customer of a local poverty alleviation shop. According to him, when he first shopped there, he was just trying to contribute his part to poverty reduction, but was later fascinated by the good quality of the products there.
"The agricultural products, such as honey pomelo and mushrooms, are directly sourced from places of origin. They are of great quality and priced fairly," Luo said.
"Internet technology will play a huge role in boosting the consumption of products from poor areas. Apart from further expanding online sales channels, it will also offer more services," said Wang Jiahua, chairman of the Social Participation in Poverty Alleviation and Development of China.
He introduced that the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development has built a fourth-party platform to boost the consumption of products from poor areas relying on the site of the Social Participation in Poverty Alleviation and Development of China. The platform offers online exhibition, expands channels, and records statistics for buyers, sellers and third parties.
As of Oct. 31, a total of 136,130 poverty relief products had been launched in 22 provinces in central and west China. Coming from 1,836 counties and 39,523 suppliers, they generated revenue of over 227.6 billion yuan, which over-fulfilled the annual task of 200 billion yuan.
These pro-consumption campaigns have effectively opened up the market of agricultural products, offsetting the negative impacts from COVID-19.
A trade fair was recently held in Bozhou, east China's Anhui province to facilitate the sales of local products for poverty alleviation. Nearly 100 kinds of agricultural products from impoverished regions were exhibited at the fair, generating revenue of over 13.5 million yuan ($2.07 million).
Qi Yi, vice general manager of a farm produce company in Anhui, told People's Daily that the company now has employees from more than 100 impoverished households, and the good sale further enhanced its resolution to contribute to poverty alleviation efforts.
In Qixian county, central China's Henan province, impoverished resident Shan Hailong's peanuts and sweet potatoes, which weighed over 5,000 tonnes in total, were hardly sold. To solve his problem, cadres from his village and township immediately introduced him to several local supermarkets, who helped him transport and market his products.
In Nanbu county, southwest China's Sichuan province, a vast orange orchard is cultivated by a local cooperative. According to Luo Qiang, an executive of the cooperative, the orchard is a poverty alleviation program under the coordination between Nanbu county and Dongtou village, Wenzhou, east China's Zhejiang province. The trees are "adopted" by consumers online, and entrusted to the cooperative for management, and the fruits in the orchard all have a QR code that tells their growth and sales.
"Thanks to pro-consumption campaigns to aid poverty alleviation, these fruits are all sold at a pretty good price," Luo said.
The orchard is only one of the many examples of poverty reduction cooperation. A supermarket in Xiamen, southeast China's Fujian province, now runs a special section that sells farm produce from Linxia prefecture, northwest China's Gansu province. "The vegetables from the plateau area enjoy great sunshine and are free from pollution. They taste great," said citizen Zhang Juan, adding that it's also a contribution to poverty alleviation to buy these vegetables.
The pro-consumption campaigns to aid poverty alleviation are never once-for-all deals, and they are gaining more and more returned customers. Luo Zhiyuan from Ji'an, east China's Jiangxi province, is a frequent customer of a local poverty alleviation shop. According to him, when he first shopped there, he was just trying to contribute his part to poverty reduction, but was later fascinated by the good quality of the products there.
"The agricultural products, such as honey pomelo and mushrooms, are directly sourced from places of origin. They are of great quality and priced fairly," Luo said.
"Internet technology will play a huge role in boosting the consumption of products from poor areas. Apart from further expanding online sales channels, it will also offer more services," said Wang Jiahua, chairman of the Social Participation in Poverty Alleviation and Development of China.
He introduced that the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development has built a fourth-party platform to boost the consumption of products from poor areas relying on the site of the Social Participation in Poverty Alleviation and Development of China. The platform offers online exhibition, expands channels, and records statistics for buyers, sellers and third parties.
As of Oct. 31, a total of 136,130 poverty relief products had been launched in 22 provinces in central and west China. Coming from 1,836 counties and 39,523 suppliers, they generated revenue of over 227.6 billion yuan, which over-fulfilled the annual task of 200 billion yuan.
 Menu
Menu
 China boosts consumption of products from poor areas to help poverty alleviation
China boosts consumption of products from poor areas to help poverty alleviation