By Liu Shiyao, People's Daily
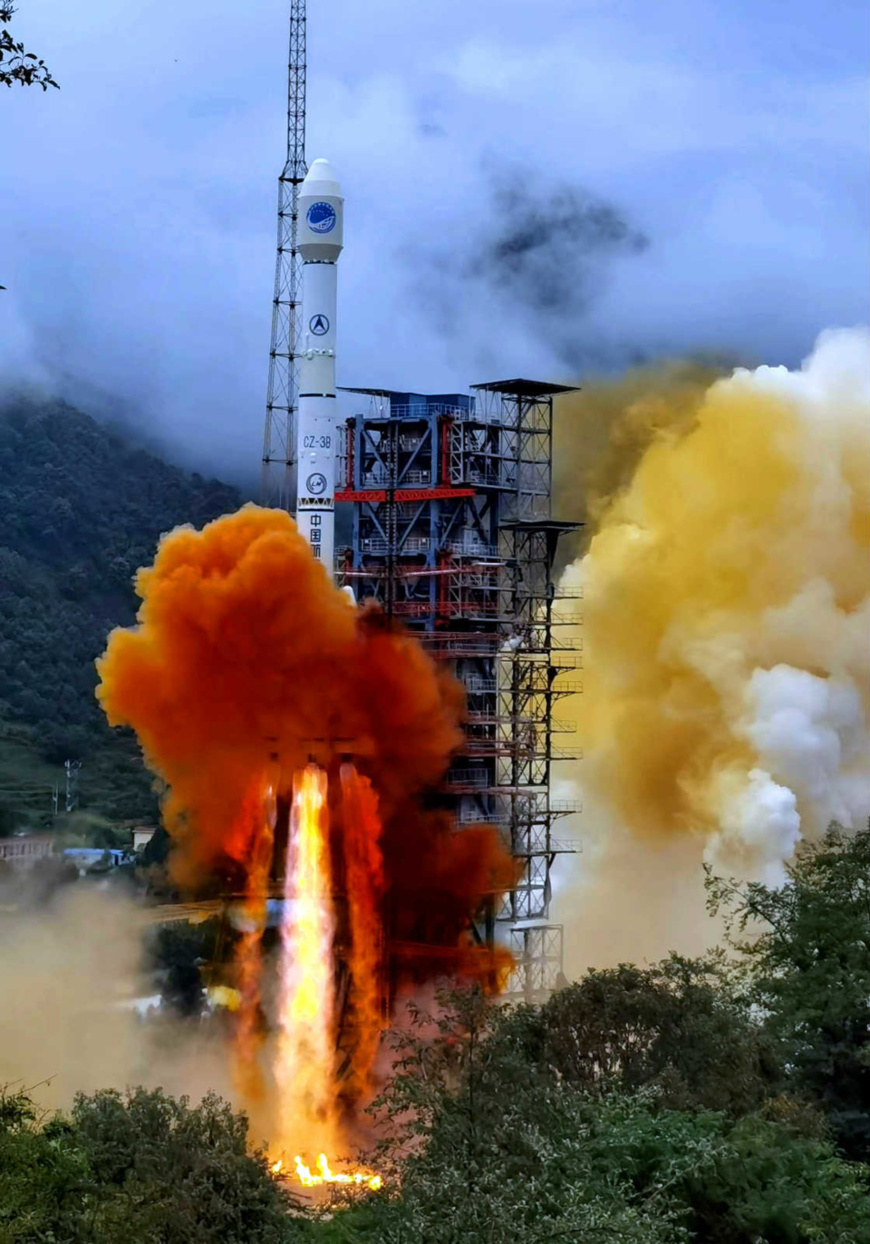

A carrier rocket carrying the last satellite of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System blasts off from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Southwest China's Sichuan Province, June 23. (Photo by Li Jieyi/People's Daily Online)
China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) was officially commissioned recently, which marked a success of the country's three-step strategy for developing the navigation satellite system and a start of the system's global service.
Starting in November 2009, the construction of the BDS-3 went through five stages, including tackling key technologies, testing satellite projects, as well as the building of simple, basic and complete systems. The constellation deployment of the BDS-3 was finished half a year in advance, which enabled the system to start full service.
The BDS-3 system involves efforts of more than 400 agencies and 300,000 research personnel and technicians, who tackled more than 160 key core technologies, from inter-satellite links to high-precision atomic clocks, and localized the production of over 500 types of equipment component. All key components of the BDS-3 were manufactured by China.
The lead time of a single satellite was reduced by 1/4, the general assembly time for carrier rockets by 1/3, and the time needed for satellites to join the constellation by 3/4.
The BDS-3 combines navigation and communication capabilities, and can provide services of navigation, short message communication, satellite-based augmentation, international search and rescue, as well as precise point positioning. All the services are covered by the Interface Control Document the system has published.
The BDS-3 has a high performance, with positioning accuracy less than 10 meters, velocity measurement accuracy less than 0.2 meter per second, timing accuracy less than 20 nanoseconds, and service availability of over 99 percent. It functions better in the Asia-Pacific region.
Short message communication and high-accuracy application are the two major features of the BDS-3. Short message communication allows users to send up to 1,000 Chinese characters (14,000 bytes) per message at most at one time, as well as pictures and voice messages. With global inter-satellite links, the system also offers global message communication services.
Based on the BDS-3, a high-accuracy augmentation network has been built on the ground with a total of nearly 3,000 ground stations. The network is able to detect abnormal movements at centimeter level in real-time, and millimeter level in post-analysis.
Ran Chengqi, Director General of China Satellite Navigation Office and the spokesperson of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, introduced that the Chinese navigation system has been applied in industries such as transportation, public security, disaster relief, farming and urban governance, and has been integrated into China's key basic infrastructure construction, including electricity, finance and telecom.
Ran said 28-nanometre chips that enable mobile devices to receive signals from the Beidou navigation system are in mass production, and mass manufacturing of high-precision 22-nanometre positioning chips will soon kick off, adding that a complete industrial chain of chips, modules, boards, terminals, operation services for Beidou has been built.
In the past decade, the total output value of China’s satellite navigation and location services industry has been growing at an average annual rate of more than 20 percent, reaching 345 billion yuan ($49.47 billion) in 2019 and is expected to exceed 400 billion yuan this year, Ran said. As the Beidou navigation system steps up its efforts on new infrastructure, it is undergoing in-depth integration with new technologies such as new-generation communication, block chain, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence.
As one of the four major global satellite navigation systems recognized by the United Nations, Beidou has been constantly deepening its compatibility, interoperability and cooperation with the United States' GPS, Russia's GLONASS and the EU's Galileo. It has also entered international organizations of civil aviation, maritime affairs, search and rescue satellite, and mobile communication. Multiple international standards related to BDS have been released. So far, China has exported its basic products of the Beidou Navigation Satellite System to more than 120 countries and regions, offering services for over 100 million users.
According to Ran, China has started construction of the next-generation Beidou navigation after the completion of the BDS-3.
"A more ubiquitous, integrated and intelligent navigation and timing system with comprehensive national positioning is scheduled to be established by 2035, so as to offer supports for future smart and unmanned development, promote upgrading of the system, integrate emerging technologies, develop quantum navigation and all-source navigation, and build a time and space services infrastructure that is all-dimensional, standardized, high-accuracy, smart, secure and efficient," Ran said.
Starting in November 2009, the construction of the BDS-3 went through five stages, including tackling key technologies, testing satellite projects, as well as the building of simple, basic and complete systems. The constellation deployment of the BDS-3 was finished half a year in advance, which enabled the system to start full service.
The BDS-3 system involves efforts of more than 400 agencies and 300,000 research personnel and technicians, who tackled more than 160 key core technologies, from inter-satellite links to high-precision atomic clocks, and localized the production of over 500 types of equipment component. All key components of the BDS-3 were manufactured by China.
The lead time of a single satellite was reduced by 1/4, the general assembly time for carrier rockets by 1/3, and the time needed for satellites to join the constellation by 3/4.
The BDS-3 combines navigation and communication capabilities, and can provide services of navigation, short message communication, satellite-based augmentation, international search and rescue, as well as precise point positioning. All the services are covered by the Interface Control Document the system has published.
The BDS-3 has a high performance, with positioning accuracy less than 10 meters, velocity measurement accuracy less than 0.2 meter per second, timing accuracy less than 20 nanoseconds, and service availability of over 99 percent. It functions better in the Asia-Pacific region.
Short message communication and high-accuracy application are the two major features of the BDS-3. Short message communication allows users to send up to 1,000 Chinese characters (14,000 bytes) per message at most at one time, as well as pictures and voice messages. With global inter-satellite links, the system also offers global message communication services.
Based on the BDS-3, a high-accuracy augmentation network has been built on the ground with a total of nearly 3,000 ground stations. The network is able to detect abnormal movements at centimeter level in real-time, and millimeter level in post-analysis.
Ran Chengqi, Director General of China Satellite Navigation Office and the spokesperson of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, introduced that the Chinese navigation system has been applied in industries such as transportation, public security, disaster relief, farming and urban governance, and has been integrated into China's key basic infrastructure construction, including electricity, finance and telecom.
Ran said 28-nanometre chips that enable mobile devices to receive signals from the Beidou navigation system are in mass production, and mass manufacturing of high-precision 22-nanometre positioning chips will soon kick off, adding that a complete industrial chain of chips, modules, boards, terminals, operation services for Beidou has been built.
In the past decade, the total output value of China’s satellite navigation and location services industry has been growing at an average annual rate of more than 20 percent, reaching 345 billion yuan ($49.47 billion) in 2019 and is expected to exceed 400 billion yuan this year, Ran said. As the Beidou navigation system steps up its efforts on new infrastructure, it is undergoing in-depth integration with new technologies such as new-generation communication, block chain, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence.
As one of the four major global satellite navigation systems recognized by the United Nations, Beidou has been constantly deepening its compatibility, interoperability and cooperation with the United States' GPS, Russia's GLONASS and the EU's Galileo. It has also entered international organizations of civil aviation, maritime affairs, search and rescue satellite, and mobile communication. Multiple international standards related to BDS have been released. So far, China has exported its basic products of the Beidou Navigation Satellite System to more than 120 countries and regions, offering services for over 100 million users.
According to Ran, China has started construction of the next-generation Beidou navigation after the completion of the BDS-3.
"A more ubiquitous, integrated and intelligent navigation and timing system with comprehensive national positioning is scheduled to be established by 2035, so as to offer supports for future smart and unmanned development, promote upgrading of the system, integrate emerging technologies, develop quantum navigation and all-source navigation, and build a time and space services infrastructure that is all-dimensional, standardized, high-accuracy, smart, secure and efficient," Ran said.
 Menu
Menu
 China exports Beidou system products to over 120 countries and regions
China exports Beidou system products to over 120 countries and regions