By Zou Yating, People's Daily
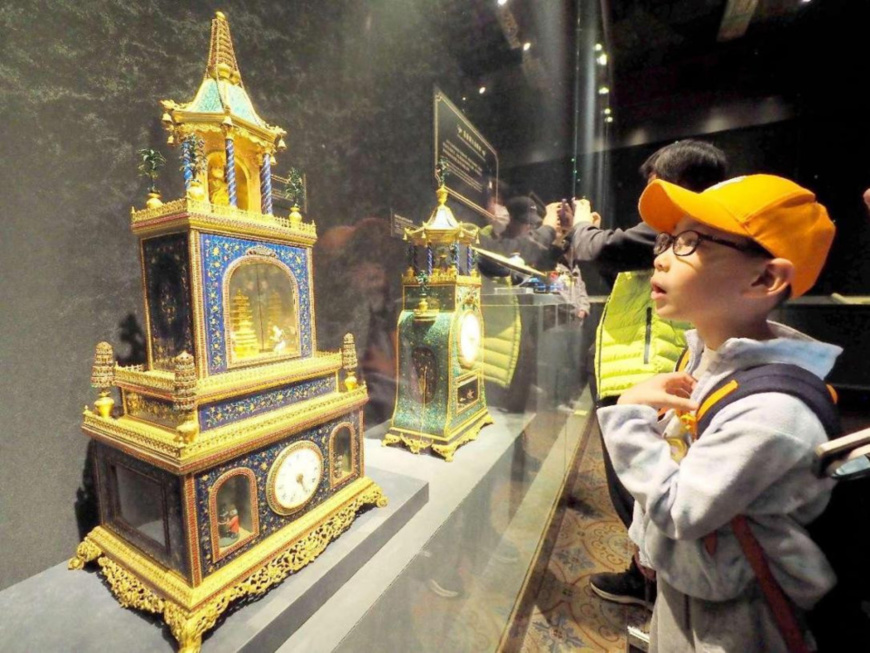

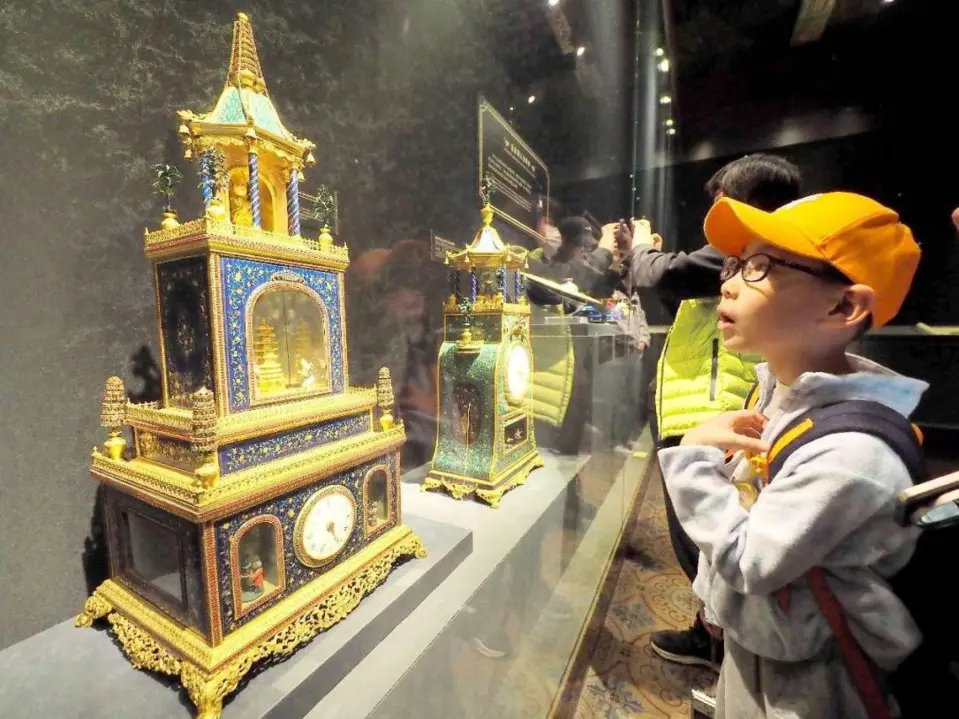
People visit the exhibition "The Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles: Exchanges Between China and France in the 17th and 18th Centuries" in the Hall of Literary Glory (Wenhuadian) of the Palace Museum, April 2, 2024. (Photo by Du Jianpo/People's Daily Online)
An exhibition focusing on the exchanges between China and France in the 17th and 18th centuries recently kicked off in the Hall of Literary Glory (Wenhuadian) of the Palace Museum in Beijing, capital of China.
The exhibition "The Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles: Exchanges Between China and France in the 17th and 18th Centuries" was jointly held by the Palace Museum and the Palace of Versailles.
It features about 200 works from the collections of the two museums and other institutions, attracting many who are interested in Chinese and French cultures.
In the second half of the 17th century and the 18th century, centered around the Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles, there were extensive and profound exchanges of personnel, ideas, and cultures between the two countries.
The exhibition showcases some rare ancient books including "Nouveaux Mémoires sur l'état présent de la Chine" by Louis Le Comte and a collection of correspondence by French astronomer Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan. These books have provided information about China, disseminated Chinese culture, and deepened Europe's understanding of China, leaving a profound impact on Europe.
"From the rich cultural relics, it can be seen that the exchanges of science and art made up the majority of China-France exchanges in the 17th and 18th centuries," said Guo Fuxiang, a research fellow at the Palace Museum and the Chinese curator of the exhibition.
Inside a black lacquered square box exhibited, there are more than 30 instruments, including a plotting scale, a ruler, a carpenter's square, a compass, a protractor, and more. The box also contains a copper-gilded triangular stand and a blue enamel water container.
These drafting instruments, comprised of both Chinese- and French made ones selected by the imperial workshop of the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), make up a complete and practical set.
French culture had a significant influence on the science, art, architecture, medicine, and cartography development of the Qing dynasty, as reflected by the items collected by the Palace Museum, including Euclid's Elements and Si yang-ni okto-i bithe (Handbook of Western Drugs) in Manchu language, the etchings of structures in the Yuanmingyuan Park, or the Old Summer Palace, as well as French clocks, multifunctional mirrors and essential oil.
At the same time, a large number of Chinese handicrafts and books entered France, sparking a "Chinese-style art" trend centered around the Palace of Versailles and spreading to various European countries.
Chinese porcelain was highly admired by Europeans, and the French would even decorate and modify porcelain ware to better suit their taste. For instance, Parisian craftsmen added Rococo-style gilded copper ornaments to the top, rim, and base of Chinese celadon perfume bottles, giving them a fountain-like shape.
In addition to porcelain, the French actively drew inspiration from Chinese culture in various fields such as painting, textiles, lacquerware, architecture, and gardens. China became an important source of inspiration for French artists and intellectuals.
An engraving in the 17th century just depicted how beautiful the Trianon de Porcelaine was. Inspired by the Porcelain Tower of Nanjing in China, France built the Trianon de Porcelaine in 1670. Located on the outskirts of the Palace of Versailles, the Trianon de Porcelaine was adorned with blue and white ceramics, with ornate roofs featuring vases, children, and animal figures. The interior of the palace was decorated with silk fabrics featuring Chinese floral patterns.
Cultural exchange has never been a one-way process, but rather a dynamic interaction that sparks innovation and vitality.
In the second half of the 17th century, France began to take an interest in and study Chinese porcelain-making craft. In the mid-18th century, with the discovery of kaolin deposits, the Manufacture nationale de Sevres of France successfully produced hard-paste porcelain. The shapes and decorative patterns of these porcelain pieces were heavily influenced by Chinese porcelain, yet they also possessed their own unique characteristics. France presented Sevres porcelain masterpieces as diplomatic gifts to other countries, including China.
"Although China and France are thousands of miles away from each other, they have had continuous cultural exchanges throughout history," said Guo. Even today, this interaction and exchange are remembered and constantly writing new chapters.
The Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles are witnesses to the historical exchanges between China and France, as well as symbols of their respective cultures. Today, they continue to tell stories of mutual learning and exchange.
Wang Xudong, director of the Palace Museum, noted that through the exhibition of precious cultural relics, people can appreciate the history of cultural exchanges between China and France, in which the two countries have learned from each other. This exchange has not only had a significant impact on the cultures of both countries but also provided an example of mutual learning and exchange between civilizations.
The exhibition "The Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles: Exchanges Between China and France in the 17th and 18th Centuries" was jointly held by the Palace Museum and the Palace of Versailles.
It features about 200 works from the collections of the two museums and other institutions, attracting many who are interested in Chinese and French cultures.
In the second half of the 17th century and the 18th century, centered around the Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles, there were extensive and profound exchanges of personnel, ideas, and cultures between the two countries.
The exhibition showcases some rare ancient books including "Nouveaux Mémoires sur l'état présent de la Chine" by Louis Le Comte and a collection of correspondence by French astronomer Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan. These books have provided information about China, disseminated Chinese culture, and deepened Europe's understanding of China, leaving a profound impact on Europe.
"From the rich cultural relics, it can be seen that the exchanges of science and art made up the majority of China-France exchanges in the 17th and 18th centuries," said Guo Fuxiang, a research fellow at the Palace Museum and the Chinese curator of the exhibition.
Inside a black lacquered square box exhibited, there are more than 30 instruments, including a plotting scale, a ruler, a carpenter's square, a compass, a protractor, and more. The box also contains a copper-gilded triangular stand and a blue enamel water container.
These drafting instruments, comprised of both Chinese- and French made ones selected by the imperial workshop of the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), make up a complete and practical set.
French culture had a significant influence on the science, art, architecture, medicine, and cartography development of the Qing dynasty, as reflected by the items collected by the Palace Museum, including Euclid's Elements and Si yang-ni okto-i bithe (Handbook of Western Drugs) in Manchu language, the etchings of structures in the Yuanmingyuan Park, or the Old Summer Palace, as well as French clocks, multifunctional mirrors and essential oil.
At the same time, a large number of Chinese handicrafts and books entered France, sparking a "Chinese-style art" trend centered around the Palace of Versailles and spreading to various European countries.
Chinese porcelain was highly admired by Europeans, and the French would even decorate and modify porcelain ware to better suit their taste. For instance, Parisian craftsmen added Rococo-style gilded copper ornaments to the top, rim, and base of Chinese celadon perfume bottles, giving them a fountain-like shape.
In addition to porcelain, the French actively drew inspiration from Chinese culture in various fields such as painting, textiles, lacquerware, architecture, and gardens. China became an important source of inspiration for French artists and intellectuals.
An engraving in the 17th century just depicted how beautiful the Trianon de Porcelaine was. Inspired by the Porcelain Tower of Nanjing in China, France built the Trianon de Porcelaine in 1670. Located on the outskirts of the Palace of Versailles, the Trianon de Porcelaine was adorned with blue and white ceramics, with ornate roofs featuring vases, children, and animal figures. The interior of the palace was decorated with silk fabrics featuring Chinese floral patterns.
Cultural exchange has never been a one-way process, but rather a dynamic interaction that sparks innovation and vitality.
In the second half of the 17th century, France began to take an interest in and study Chinese porcelain-making craft. In the mid-18th century, with the discovery of kaolin deposits, the Manufacture nationale de Sevres of France successfully produced hard-paste porcelain. The shapes and decorative patterns of these porcelain pieces were heavily influenced by Chinese porcelain, yet they also possessed their own unique characteristics. France presented Sevres porcelain masterpieces as diplomatic gifts to other countries, including China.
"Although China and France are thousands of miles away from each other, they have had continuous cultural exchanges throughout history," said Guo. Even today, this interaction and exchange are remembered and constantly writing new chapters.
The Forbidden City and the Palace of Versailles are witnesses to the historical exchanges between China and France, as well as symbols of their respective cultures. Today, they continue to tell stories of mutual learning and exchange.
Wang Xudong, director of the Palace Museum, noted that through the exhibition of precious cultural relics, people can appreciate the history of cultural exchanges between China and France, in which the two countries have learned from each other. This exchange has not only had a significant impact on the cultures of both countries but also provided an example of mutual learning and exchange between civilizations.
 Menu
Menu
 Exhibition on China-France exchanges in 17th, 18th centuries hosted at Palace Museum
Exhibition on China-France exchanges in 17th, 18th centuries hosted at Palace Museum