By Gu Yekai, People's Daily
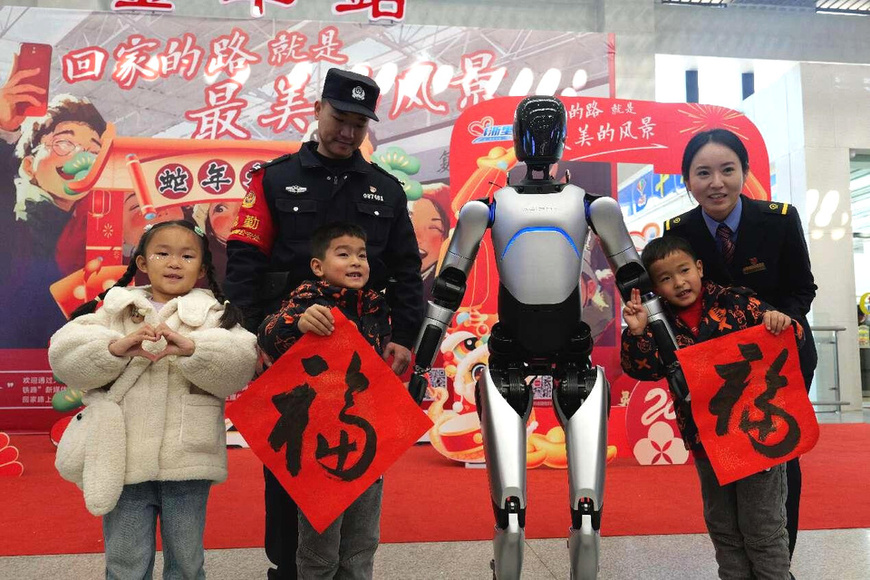

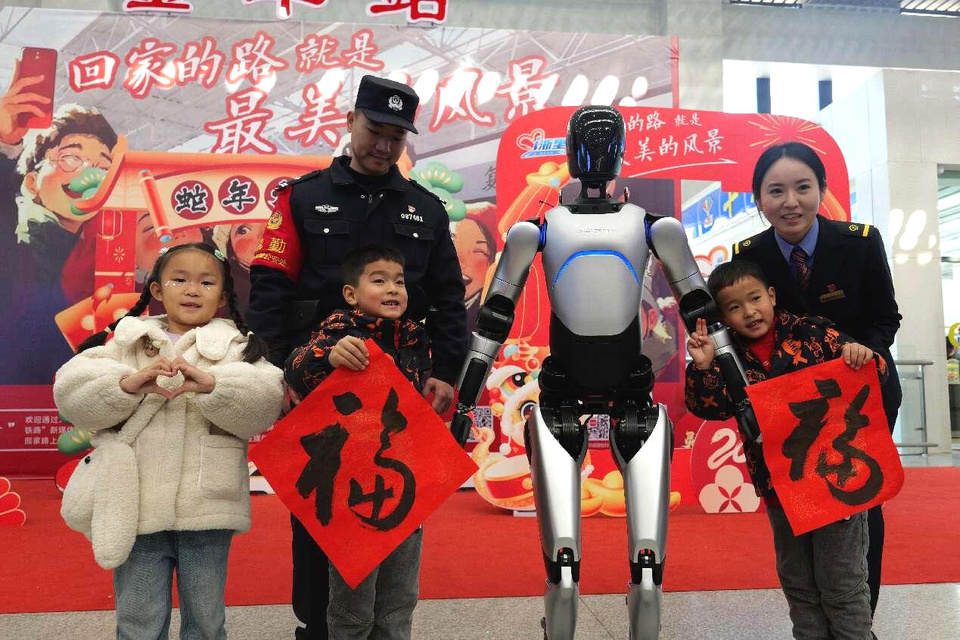
A smart robot poses for a picture in a waiting hall of the Jinhua Railway Station in east China's Zhejiang province, Jan. 14, 2025. (Photo by Pan Qiuya/People's Daily Online)
Modern scientific research increasingly depends on advanced research tools. In particular, large-scale scientific facilities play a crucial role in exploring the unknown, uncovering natural laws, and propelling technological progress.
In recent times, notable scientific breakthroughs have been made in connection with large-scale scientific facilities. For instance, Chinese researchers, during the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment at the European Organization for Nuclear Research, have attained the most precise measurement of the parity violation parameter to date. This parameter, also referred to as the "Lee-Yang" parameter, was originally proposed by physicists Tsung-Dao Lee and Yang Chen-Ning in 1956.
The construction of large-scale scientific facilities is advancing at a rapid pace in China. The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), known as China's "artificial sun" in Hefei, east China's Anhui province, has recently made significant strides in research. Scientists have successfully conducted experiments utilizing a newly constructed large-scale superconducting magnet dynamic performance test system. This achievement has established a solid foundation for the future development of fusion reactor components.
Besides, the Advanced Attosecond Laser Infrastructure is under construction in Dongguan, south China's Guangdong province. By utilizing attosecond laser pulses, scientists can track, measure, and manipulate the motion of electrons, akin to capturing the "dynamic images" of electrons using a "high-speed camera." An attosecond is the shortest time scale currently mastered by humans, with one attosecond being only one quintillionth of a second. It is truly the epitome of a "fleeting moment."
In addition to pushing the boundaries of science, many technological challenges crucial for economic and social development are being addressed with the help of large-scale scientific facilities.
A recent example is the utilization of the China Spallation Neutron Source, often referred to as a "super microscope," in the testing of large-caliber high-grade oil and gas pipelines. This advanced facility has played a key role in enabling precise evaluation of the reliability of circumferential weld joints, optimizing welding processes, and enhancing the safety of oil and gas operations.
When discussing "scientific tools," it is impossible to overlook the current buzz surrounding AI. In recent years, scientists have been exploring the simulation of life systems through innovative approaches like synthetic biology. Recently, a Japanese company introduced a cutting-edge technology that leverages visual language-based models to autonomously search for and identify novel artificial life forms. This groundbreaking technology eliminates the need for laborious manual design processes, thereby expanding the potential for uncovering previously unknown life forms.
Scientific discovery is a multifaceted journey that can be propelled by cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, as well as the tireless efforts of dedicated scientists. Recently, a collaborative research effort between the China University of Geosciences (Beijing) and the China Geological Survey led to a remarkable find in Changdu, Xizang autonomous region: the world's smallest sauropod footprints. Measuring a mere 8.8 centimeters, these miniature footprints have significantly contributed to people's knowledge of dinosaurs.
The recently held 2025 Consumer Electronics Show has become a hub for cutting-edge technological innovations, with a particular focus on the widespread integration of AI.
Chinese companies have notably showcased their advancements in AI technology, elevating the quality and sophistication of products under the "Made in China" label. One standout example was the modular AI companion robot presented by Chinese tech firm TCL, which has garnered significant attention for its charming design and its capacity to engage in seamless, natural interactions with humans across various modes while offering emotional support and companionship.
The emergence of robots capable of providing emotional support raises intriguing questions about their possession of emotional intelligence, a subject currently under scientific investigation. Emotional intelligence represents a promising technological frontier that enables digital beings and robots to recognize emotions, express emotions, and form emotional bonds. This capability holds great potential for diverse applications in sectors like healthcare and education.
However, the advancement of emotional intelligence in AI must place a strong emphasis on establishing clear boundaries, as concerns surrounding privacy, safety, and ethical implications are set to become pivotal within the industry. It is imperative for legal regulations and policy frameworks to adapt to these developments. While the prospect of more empathetic "cyber friends" is exciting, it is crucial to recognize that the decisions made today will shape the future of humanity.
In recent times, notable scientific breakthroughs have been made in connection with large-scale scientific facilities. For instance, Chinese researchers, during the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment at the European Organization for Nuclear Research, have attained the most precise measurement of the parity violation parameter to date. This parameter, also referred to as the "Lee-Yang" parameter, was originally proposed by physicists Tsung-Dao Lee and Yang Chen-Ning in 1956.
The construction of large-scale scientific facilities is advancing at a rapid pace in China. The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), known as China's "artificial sun" in Hefei, east China's Anhui province, has recently made significant strides in research. Scientists have successfully conducted experiments utilizing a newly constructed large-scale superconducting magnet dynamic performance test system. This achievement has established a solid foundation for the future development of fusion reactor components.
Besides, the Advanced Attosecond Laser Infrastructure is under construction in Dongguan, south China's Guangdong province. By utilizing attosecond laser pulses, scientists can track, measure, and manipulate the motion of electrons, akin to capturing the "dynamic images" of electrons using a "high-speed camera." An attosecond is the shortest time scale currently mastered by humans, with one attosecond being only one quintillionth of a second. It is truly the epitome of a "fleeting moment."
In addition to pushing the boundaries of science, many technological challenges crucial for economic and social development are being addressed with the help of large-scale scientific facilities.
A recent example is the utilization of the China Spallation Neutron Source, often referred to as a "super microscope," in the testing of large-caliber high-grade oil and gas pipelines. This advanced facility has played a key role in enabling precise evaluation of the reliability of circumferential weld joints, optimizing welding processes, and enhancing the safety of oil and gas operations.
When discussing "scientific tools," it is impossible to overlook the current buzz surrounding AI. In recent years, scientists have been exploring the simulation of life systems through innovative approaches like synthetic biology. Recently, a Japanese company introduced a cutting-edge technology that leverages visual language-based models to autonomously search for and identify novel artificial life forms. This groundbreaking technology eliminates the need for laborious manual design processes, thereby expanding the potential for uncovering previously unknown life forms.
Scientific discovery is a multifaceted journey that can be propelled by cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, as well as the tireless efforts of dedicated scientists. Recently, a collaborative research effort between the China University of Geosciences (Beijing) and the China Geological Survey led to a remarkable find in Changdu, Xizang autonomous region: the world's smallest sauropod footprints. Measuring a mere 8.8 centimeters, these miniature footprints have significantly contributed to people's knowledge of dinosaurs.
The recently held 2025 Consumer Electronics Show has become a hub for cutting-edge technological innovations, with a particular focus on the widespread integration of AI.
Chinese companies have notably showcased their advancements in AI technology, elevating the quality and sophistication of products under the "Made in China" label. One standout example was the modular AI companion robot presented by Chinese tech firm TCL, which has garnered significant attention for its charming design and its capacity to engage in seamless, natural interactions with humans across various modes while offering emotional support and companionship.
The emergence of robots capable of providing emotional support raises intriguing questions about their possession of emotional intelligence, a subject currently under scientific investigation. Emotional intelligence represents a promising technological frontier that enables digital beings and robots to recognize emotions, express emotions, and form emotional bonds. This capability holds great potential for diverse applications in sectors like healthcare and education.
However, the advancement of emotional intelligence in AI must place a strong emphasis on establishing clear boundaries, as concerns surrounding privacy, safety, and ethical implications are set to become pivotal within the industry. It is imperative for legal regulations and policy frameworks to adapt to these developments. While the prospect of more empathetic "cyber friends" is exciting, it is crucial to recognize that the decisions made today will shape the future of humanity.
 Menu
Menu
 Large-scale scientific facilities contribute to technological progress
Large-scale scientific facilities contribute to technological progress