By Jin Xin, Ni Ge, People's Daily
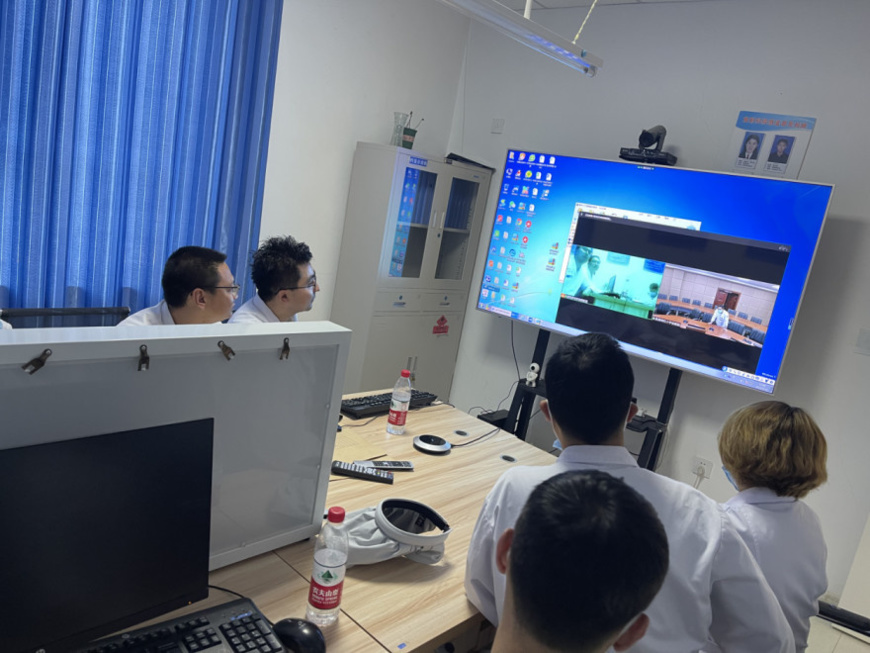

A remote group consultation is carried out between a hospital in Aksu, northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region and Hangzhou Red Cross Hospital in east China's Zhejiang province. (Photo from the official account of the command center of Zhejiang province's paired assistance program for Xizang autonomous region's Nagqu on WeChat)
A 5G ultra-remote robotic liver tumor resection surgery was recently completed, with the surgeon in east China's Zhejiang province and the patient in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region nearly 5,000 kilometers away.
The surgeon, form a surgical control station, operated robotic arms skillfully, and the robotic arms, upon receiving the commands, precisely executed various surgical tasks.
So far, hospitals in Zhejiang have completed over 50 such 5G ultra-remote robotic surgeries for patients in Xinjiang.
In recent years, telemedicine and digital healthcare have rapidly developed in China, safeguarding public health and vividly illustrating how information technology promotes equitable public services and fosters inclusive development of the internet.
In 2010, Zhejiang started offering paired assistance for Xinjiang's Aksu region and the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps.
Since then, leveraging network communication technology, doctors from Zhejiang have implemented remote consultations and transmitted medical images, among other healthcare initiatives.
"Back then, the idea of performing remote surgeries on patients in Xinjiang using robots from Zhejiang seemed like a fantasy," recalled a doctor aiding Xinjiang.
According to Li Zheyong, vice president of ALaer Hospital in Xinjiang, which supervised by the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital affiliated with Zhejiang University, School of Medicine,, communication technology is key to remote robotic surgery.
"Generally speaking, the network delay during a surgery should not exceed 300 milliseconds, and it must not be interrupted," Li said.
In recent years, mobile communication technologies such as 5G have rapidly advanced, and the infrastructure for network communication has continually improved.
As of 2023, China accounted for 42 percent of the world's essential patents for 5G standards. The country has built a total of over 3.37 million 5G base stations, and its computing power ranked second in the world. This largest and most advanced 5G network has made it possible to transcend geographical limitations.
In 2023, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital completed a 5G ultra-remote robotic cholecystectomy for a patient in Xinjiang, the first of its kind in China. The surgery utilized the country's first four-arm laparoscopic robot that employs 5G technology for ultra-remote operations, whose core software and hardware were all developed by Chinese teams.
Recently, on a desert road in Alaer city, administered by the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, a car accident took place, leading to multiple fractures of a man.
Soon after the accident took place, a doctor from a nearby health clinic arrived at the site. Lacking experience in emergency care, the doctor was concerned that improper handling could jeopardize the man's recovery.
Thanks to a pair of specially designed augmented reality (AR) glasses the doctor took, which was enabled by the 5G technology, he received guidance from experienced experts, who were observing the patient through the glasses in real time.
"The 5G + AR remote diagnosis system extends high-quality medical care to the primary level," said Cai Xiujun, president of Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital.
The application of internet technology in the healthcare sector is helping urban and rural areas better share quality medical resources, and it's not just in Xinjiang. The remote medical service network now covers all cities and counties in China and is extending to the primary level in communities and rural regions. Approximately 70 percent of primary-level clinics nationwide have established remote medical collaboration with higher-level hospitals.
The rapid advancement of the internet and the ongoing digitalization efforts are bridging the "digital divide" between urban and rural areas at an unprecedented pace, enhancing the accessibility and equality of basic public services.
"Now, tests done in cities can also have their results viewed back in rural hospitals; it’s truly convenient," said Tulfjang, a Xinjiang patient with chronic illness.
With the support from the medical teams assisting Xinjiang, Aksu region and the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps are gradually establishing a chronic disease management system that covers regional, county, township, and village levels, promoting patient information sharing, mutual recognition of testing data, and standardized management.
This integration of information goes beyond healthcare. Interconnected data improves the efficiency of government and public services, allowing more people to genuinely benefit from the digital dividends brought by technology.
The surgeon, form a surgical control station, operated robotic arms skillfully, and the robotic arms, upon receiving the commands, precisely executed various surgical tasks.
So far, hospitals in Zhejiang have completed over 50 such 5G ultra-remote robotic surgeries for patients in Xinjiang.
In recent years, telemedicine and digital healthcare have rapidly developed in China, safeguarding public health and vividly illustrating how information technology promotes equitable public services and fosters inclusive development of the internet.
In 2010, Zhejiang started offering paired assistance for Xinjiang's Aksu region and the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps.
Since then, leveraging network communication technology, doctors from Zhejiang have implemented remote consultations and transmitted medical images, among other healthcare initiatives.
"Back then, the idea of performing remote surgeries on patients in Xinjiang using robots from Zhejiang seemed like a fantasy," recalled a doctor aiding Xinjiang.
According to Li Zheyong, vice president of ALaer Hospital in Xinjiang, which supervised by the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital affiliated with Zhejiang University, School of Medicine,, communication technology is key to remote robotic surgery.
"Generally speaking, the network delay during a surgery should not exceed 300 milliseconds, and it must not be interrupted," Li said.
In recent years, mobile communication technologies such as 5G have rapidly advanced, and the infrastructure for network communication has continually improved.
As of 2023, China accounted for 42 percent of the world's essential patents for 5G standards. The country has built a total of over 3.37 million 5G base stations, and its computing power ranked second in the world. This largest and most advanced 5G network has made it possible to transcend geographical limitations.
In 2023, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital completed a 5G ultra-remote robotic cholecystectomy for a patient in Xinjiang, the first of its kind in China. The surgery utilized the country's first four-arm laparoscopic robot that employs 5G technology for ultra-remote operations, whose core software and hardware were all developed by Chinese teams.
Recently, on a desert road in Alaer city, administered by the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, a car accident took place, leading to multiple fractures of a man.
Soon after the accident took place, a doctor from a nearby health clinic arrived at the site. Lacking experience in emergency care, the doctor was concerned that improper handling could jeopardize the man's recovery.
Thanks to a pair of specially designed augmented reality (AR) glasses the doctor took, which was enabled by the 5G technology, he received guidance from experienced experts, who were observing the patient through the glasses in real time.
"The 5G + AR remote diagnosis system extends high-quality medical care to the primary level," said Cai Xiujun, president of Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital.
The application of internet technology in the healthcare sector is helping urban and rural areas better share quality medical resources, and it's not just in Xinjiang. The remote medical service network now covers all cities and counties in China and is extending to the primary level in communities and rural regions. Approximately 70 percent of primary-level clinics nationwide have established remote medical collaboration with higher-level hospitals.
The rapid advancement of the internet and the ongoing digitalization efforts are bridging the "digital divide" between urban and rural areas at an unprecedented pace, enhancing the accessibility and equality of basic public services.
"Now, tests done in cities can also have their results viewed back in rural hospitals; it’s truly convenient," said Tulfjang, a Xinjiang patient with chronic illness.
With the support from the medical teams assisting Xinjiang, Aksu region and the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps are gradually establishing a chronic disease management system that covers regional, county, township, and village levels, promoting patient information sharing, mutual recognition of testing data, and standardized management.
This integration of information goes beyond healthcare. Interconnected data improves the efficiency of government and public services, allowing more people to genuinely benefit from the digital dividends brought by technology.
 Menu
Menu
 Prospering telemedicine a reflection of China's rapid internet development
Prospering telemedicine a reflection of China's rapid internet development