By Gu Yekai, People's Daily
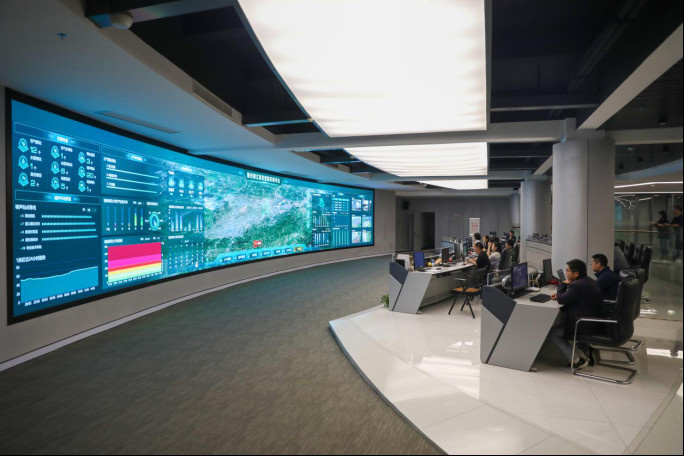

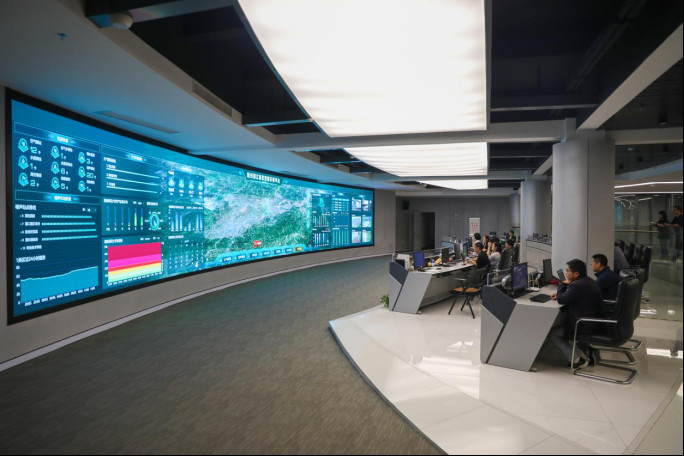
Photo taken on April 13, 2023 shows the control center of an intelligent urban management platform in the Rongjiang New Area, Ganzhou, east China's Jiangxi province. (Photo by Zhong Wanshan/People's Daily Online)
Modern cities are complex and open systems. In recent years, the rapid development and wide application of the digital twin technology are bringing new ideas and solutions to China's urban planning, governance and management.
And how traffic congestion has been relieved near the Peking University People's Hospital in Beijing's Xicheng district is a great example.
It was recently found that the long lines of cars stuck near the hospital have disappeared, and the traffic on surrounding roads has got better. It used to take more than an hour for a vehicle to wait in line before entering the hospital during peak hours, but now it takes only around 10 minutes.
This is attributed to a comprehensive traffic management system adopted by the urban management committee of the district, which shows parking resources and the distribution of shared bikes around the hospital. Based on the system, traffic managers are able to make rational recommendations on drop-off locations, intelligent dispatch of shared bikes and shared parking resources of the hospital.
The digital twin technology can simulate various factors and data of cities. Cao Xinchi, vice president of CECloud, a cloud service platform developed by China Electronics Corporation, told People's Daily that a digital twin city is a virtual city built in cyberspace by digitalizing various factors of a physical city with the Internet of Things technology.
The virtual city is formed based on building information modeling and the 3D geographic information system of the physical one, Cao added.
The construction of digital twin cities has entered a "fast lane" in China. Last year, the market hit 5.1 billion yuan ($730 million) in the country, with a compound annual growth rate of 50 percent.
Creating a virtual city that corresponds to the tangible one can make urban management more efficient and is conducive to the city's sustainable development.
Jinan, east China's Shandong province, has adopted a four-dimensional information visualization system that monitors the geological environment. By obtaining information about the stratigraphic structure, lithology and karst development features, the system offers guidance on the suitability analysis of urban rail transit lines.
Based on hydrological data, meteorological data and information of urban drainage facilities, the urban management system of Guangzhou, south China's Guangdong province, launches visualized flooding simulations at flood-prone points with the help of urban hydrology model and electronic map, thus providing references for flood control and disaster relief.
Lankao county of central China's Henan province has developed an intelligent algorithm, which can deduce the operation results of different urban regulation strategies online.
Suzhou, east China's Jiangsu province has collected comprehensive and high-precision data of ancient architectures so as to better protect and repair them.
The Xiong'an New Area in north China's Hebei province is planning and building a virtual city with the physical one simultaneously.
While digital twin cities are seeing prosperous development, they also bring new challenges.
"Digital twin cities need to store, process and present massive multi-source heterogeneous data with various types and large volumes, which is a test for the platform's support capacity and network bandwidth. Besides, the visualization and real-time browsing of a huge load of spatial-temporal data, as well as the real-time updating of various types of other data also call for a high cost in hardware, time and manpower," Cao explained.
Zhou Hongyi, founder of Chinese Internet security company Qihoo 360, said digitalization is a booster for urban management, but it also magnifies issues such as data security and privacy protection.
As digitalization accelerates in urban public services, economy and industries, as well as livelihood sectors, cities will highly rely on networks, software and data, Zhou explained, adding that digital security should be made into an integral part of urban infrastructure construction.
Li Deren, academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and professor at Wuhan University, said the country should face up to new challenges and proactively advance the construction of both physical and online spaces.
He emphasized the significance of urban planning, upgrading and science-based management, so that China's urban construction can become truly intelligent with the digital twin technology.
And how traffic congestion has been relieved near the Peking University People's Hospital in Beijing's Xicheng district is a great example.
It was recently found that the long lines of cars stuck near the hospital have disappeared, and the traffic on surrounding roads has got better. It used to take more than an hour for a vehicle to wait in line before entering the hospital during peak hours, but now it takes only around 10 minutes.
This is attributed to a comprehensive traffic management system adopted by the urban management committee of the district, which shows parking resources and the distribution of shared bikes around the hospital. Based on the system, traffic managers are able to make rational recommendations on drop-off locations, intelligent dispatch of shared bikes and shared parking resources of the hospital.
The digital twin technology can simulate various factors and data of cities. Cao Xinchi, vice president of CECloud, a cloud service platform developed by China Electronics Corporation, told People's Daily that a digital twin city is a virtual city built in cyberspace by digitalizing various factors of a physical city with the Internet of Things technology.
The virtual city is formed based on building information modeling and the 3D geographic information system of the physical one, Cao added.
The construction of digital twin cities has entered a "fast lane" in China. Last year, the market hit 5.1 billion yuan ($730 million) in the country, with a compound annual growth rate of 50 percent.
Creating a virtual city that corresponds to the tangible one can make urban management more efficient and is conducive to the city's sustainable development.
Jinan, east China's Shandong province, has adopted a four-dimensional information visualization system that monitors the geological environment. By obtaining information about the stratigraphic structure, lithology and karst development features, the system offers guidance on the suitability analysis of urban rail transit lines.
Based on hydrological data, meteorological data and information of urban drainage facilities, the urban management system of Guangzhou, south China's Guangdong province, launches visualized flooding simulations at flood-prone points with the help of urban hydrology model and electronic map, thus providing references for flood control and disaster relief.
Lankao county of central China's Henan province has developed an intelligent algorithm, which can deduce the operation results of different urban regulation strategies online.
Suzhou, east China's Jiangsu province has collected comprehensive and high-precision data of ancient architectures so as to better protect and repair them.
The Xiong'an New Area in north China's Hebei province is planning and building a virtual city with the physical one simultaneously.
While digital twin cities are seeing prosperous development, they also bring new challenges.
"Digital twin cities need to store, process and present massive multi-source heterogeneous data with various types and large volumes, which is a test for the platform's support capacity and network bandwidth. Besides, the visualization and real-time browsing of a huge load of spatial-temporal data, as well as the real-time updating of various types of other data also call for a high cost in hardware, time and manpower," Cao explained.
Zhou Hongyi, founder of Chinese Internet security company Qihoo 360, said digitalization is a booster for urban management, but it also magnifies issues such as data security and privacy protection.
As digitalization accelerates in urban public services, economy and industries, as well as livelihood sectors, cities will highly rely on networks, software and data, Zhou explained, adding that digital security should be made into an integral part of urban infrastructure construction.
Li Deren, academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and professor at Wuhan University, said the country should face up to new challenges and proactively advance the construction of both physical and online spaces.
He emphasized the significance of urban planning, upgrading and science-based management, so that China's urban construction can become truly intelligent with the digital twin technology.
 Menu
Menu
 Digital twin technology builds "smarter" cities
Digital twin technology builds "smarter" cities